As your company scales globally, hiring a professional translation service provider seems like the smart next step. However, choosing between an agency and freelance translators can be challenging. Understanding the step-by-step process of professional language translation can help you determine which option is better suited to meet your needs and deliver the desired outcomes.
This step-by-step guide to the language translation process will not only help you select the right translation partner but also set realistic expectations for the project’s timelines and outcomes.
The 6 Steps That Define A Professional Translation Process
While many perceive translation as merely converting words from one language to another, the reality is far more complex.
A professional translation process is nuanced and intricate, involving several stages that ensure translations are not only linguistically accurate but also culturally appropriate. This process is designed to carefully preserve the original message’s intent at every step.
To consistently produce high quality results that meet or exceed client expectations, top translation companies adhere to structured steps including
- Content Analysis
- Pre-Translation Preparation
- Initial Translation
- Proofreading & Editing
- File Formatting & Typesetting
- Quality Assurance
Let’s discuss each step in detail.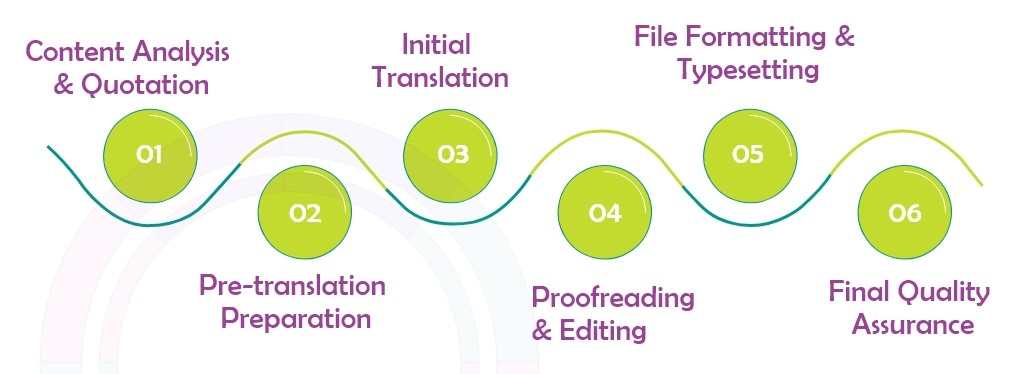
Content Analysis & Quotation
The first crucial step in any language translation process is the thorough analysis of the source text by the project managers and professional translators. When a new project is received, the translation team has to fully comprehend the meaning and purpose of the content and grasp its contextual subtleties.
They aim to gain deep insight by carefully studying the content on multiple levels:
- Is the language formal, casual, or humorous? This provides stylistic context.
- All industry-specific or technical terms are identified and defined.
- Local nuances or allusions are flagged for localization adjustments.
- Dense passages requiring additional research are noted.
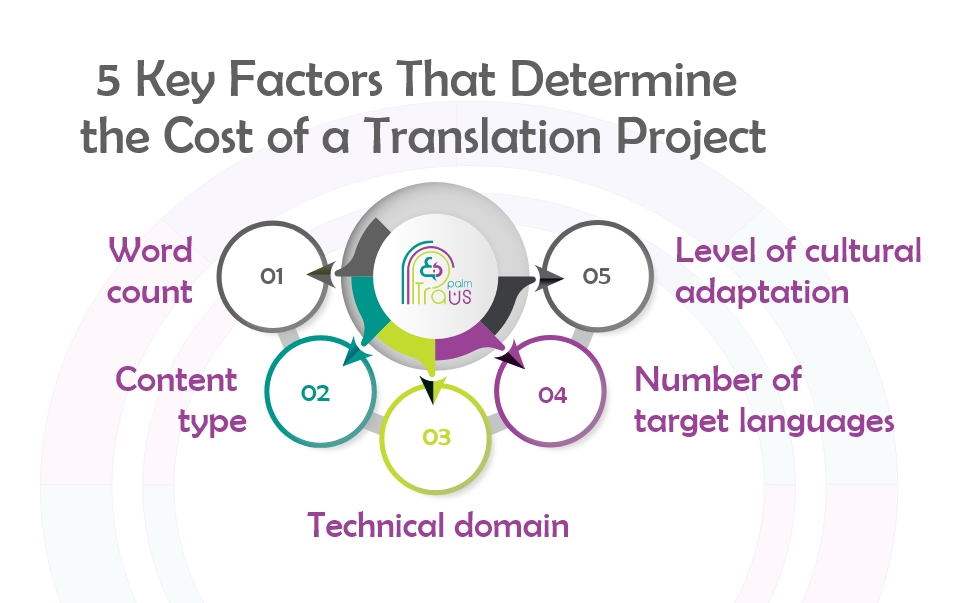
Once the content is analyzed, they generate a quote accounting for:
- Word count
- Content type
- Technical domain
- Number of target languages
- Level of cultural adaptation
Clients then receive full visibility into the translation scope and can ask clarifying questions before approving this important first step.
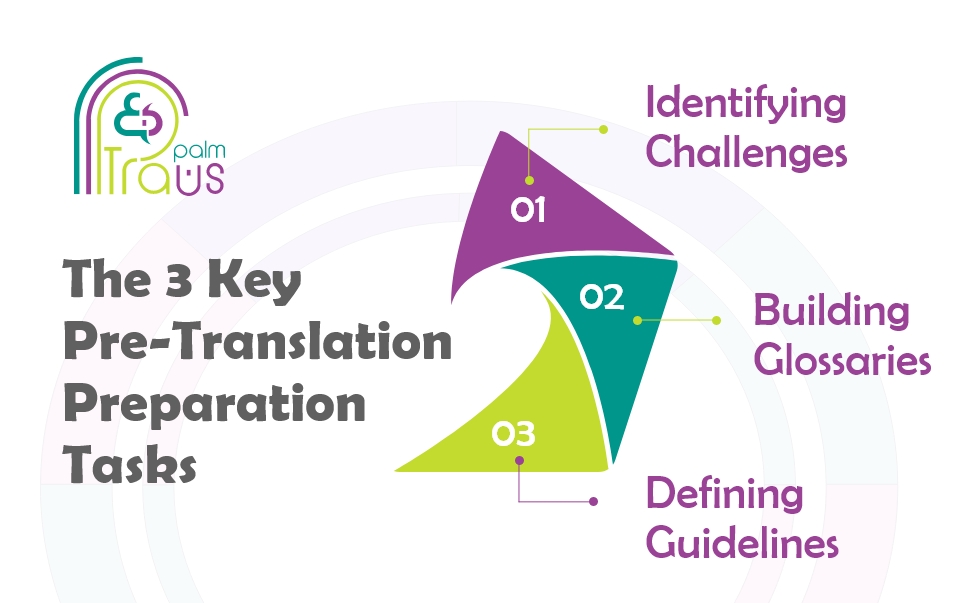
Pre-Translation Preparation
Upon confirming the project quote, the designated translators receive the source content to prepare for the translation work. This pre-translation preparation step is crucial for overcoming potential challenges.
As part of their review, translators will identify any ambiguities, lack of context, or cultural references that could hinder accurate understanding. For example, vague phrasing, undefined technical terms, or idioms specific to one language may require further explanation.
- Translators also examine readability factors like text length, the density of complex ideas, and how they flow together cohesively.
- Page layouts, images, and other design elements are accounted for as well.
After that, the translators would build comprehensive glossaries of key terminology as well as a detailed translation style guide outlining all language requirements covering tone, style, preferred phrasing, and more.
Translation
This stage is the most important and time-intensive part of the process. Now armed with the necessary guides and resources, translators begin rendering the source content into the target languages.
The primary challenge at this stage is to strike a balance between adhering to deadlines and preserving the quality of the translation.
Translators utilize two key resources to manage this balance effectively:
- Their expertise in time management
- The use of computer assisted translation (CAT) tools.
Dynamic project management ensures that translators remain focused on critical tasks, while automation aids in reducing the burden of repetitive tasks.
And although project managers provide the necessary support, the responsibility for the translation rests entirely with the translators. Their deep understanding of the subject matter and proficiency in both the source and target languages is what matters most at this step.
The Perfect Formula for Balancing Quality & Speed in Translation Professional Project Management Computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools |
Proofreading & Editing
Proofreading and editing are two critical steps in the language translation process serving as the initial quality assurance checkpoints that ensure the translated content is both accurate and contextually appropriate.
The primary purpose of proofreading and editing is to refine the translated text and eliminate any errors or mistakes that may have occurred unconsciously during the translation process including any grammatical, spelling, punctuation, and syntactic errors.
But more than just fixing mistakes, this phase also focuses on enhancing the style, coherence, and readability of the text to ensure it resonates with the target audience’s cultural and linguistic expectations and accurately conveys the intended message.
Here is an overview of the different aspects of each of the editing and proofreading steps:
| Aspect | Editing | Proofreading |
| Objective | Enhancing the linguistic quality, accuracy, and cultural appropriateness. | Checking for minor errors and polishing the text. |
| Focus | Content accuracy, style, coherence, and consistency. | Grammar, spelling, punctuation, and formatting errors. |
| When It Occurs | After the initial translation is completed. | After editing, just before finalizing the project. |
| Outcome | Ensures the translation is appropriate and resonates with the audience. | Ensures the text is error-free and professionally presented. |
File Formatting & Typesetting
Once the translation has been completed and meticulously reviewed, the subsequent phase involves formatting and typesetting the translated content to mirror the layout of the original text material. This step is crucial because clients typically expect the translated document to retain the same format as the source.
During this critical step of the language translation process, professionals make sure
- The translated text is properly integrated into the existing source design
- Elements such as font size, line spacing, and page margins are adjusted
- Any images, graphs, or tables in the original document are accurately localized in the translated version.
All of this requires strategic collaboration between graphic designers or desktop publishing specialists to ensure that the text not only fits aesthetically but also maintains readability and functional layout.
But does this really matter?
Let us give you the simplest examples.
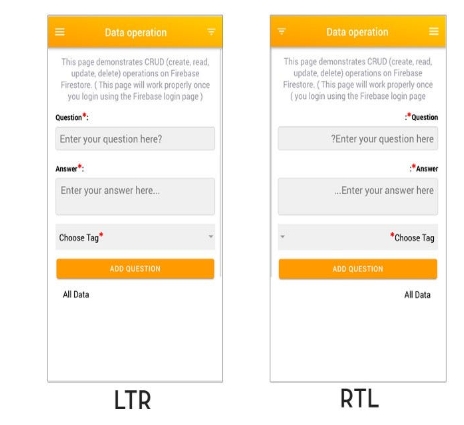
When translating between RTL and LTR languages, the content must be adapted to such structural changes post-translation. Otherwise, readers would find content distorted or difficult to consume if, for example, a RTL content was dropped directly into an LTR layout framework without adjustments.
Final Quality Assurance
In this final revision step, the quality assurance team works together and checks if there are any mistakes or errors that weren’t addressed during the editing and proofreading step. They also scrutinize the document for any typographical errors introduced during the formatting stage, paying particular attention to issues related to layout and text expansion.
Typically, it is recommended to have this review conducted by a different individual than the one who performed the initial editing and proofreading. A fresh set of eyes is more likely to spot mistakes and ensure a more thorough review.
This final screening helps guarantee the translations are delivery-ready, with issues fully addressed before handing off to clients. But while not all translation services prioritize this quality control measure, reputable agencies understand its importance
TransPalm: Your Expert Partner For All Your Multilingual Needs
We at TransPalm can save you time, money, and effort, while guaranteeing top-tier translation quality. With more than a decade of experience and proficiency in over 120 languages, our ISO-certified team is expertly equipped with the expertise and tools to deliver multilingual solutions that resonate with your business’s unique needs.
We understand the subtleties inherent in different languages and are skilled at conveying your messages accurately and effectively in every target language.
For professional translation and localization services, Contact us
Discuss Your Project with Our Experts.





