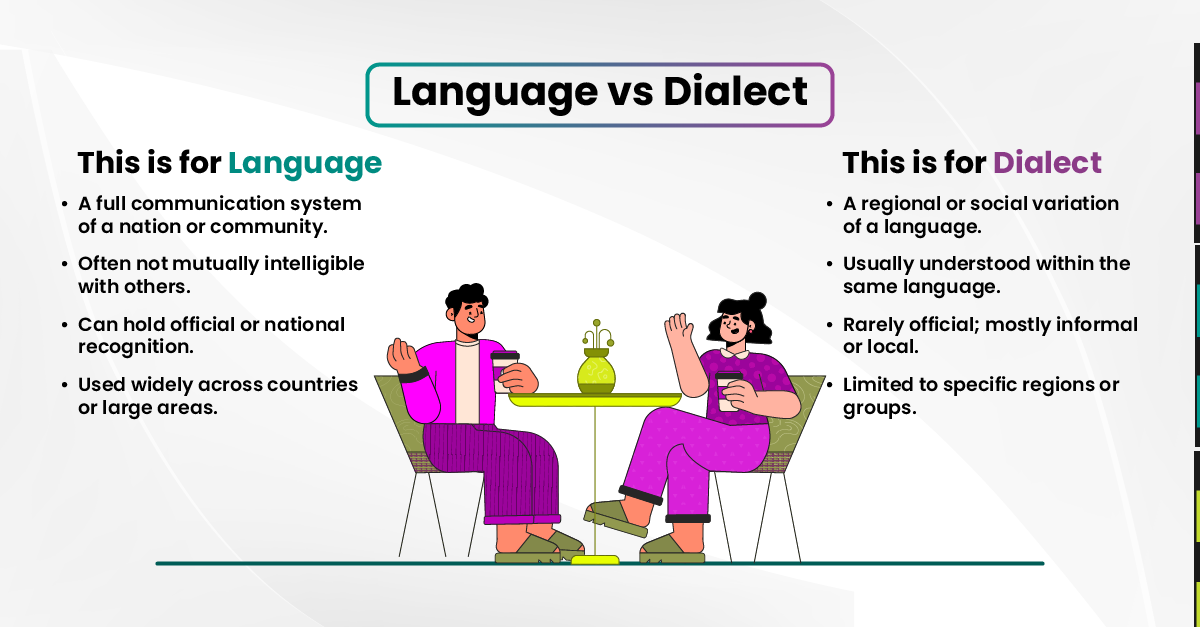
Did you know that what sounds like a completely different language may be a dialect, and what you think is just a dialect could be a separate language? In global business, this distinction can make or break your localization strategy. Misunderstanding how languages and dialects work can lead to poor word choices, missed cultural cues, and messages that fail to connect with the very people you’re trying to reach.
Dialects can shift dramatically from one region to another, even within the same country. A phrase that feels natural in one area may sound strange, overly formal, or even offensive in another. Without careful adaptation, what’s meant to be a powerful campaign can easily lose its impact or create confusion that damages brand reputation.
For global brands, distinguishing between languages and dialects is essential to avoid miscommunication and maintain brand credibility. A single phrase can carry different connotations from one region to another, making it crucial to adapt content with cultural precision. That’s why it’s so important to work with professionals who understand these fine distinctions and know how to localize your website, campaigns, marketing materials, and training programs for every audience you serve.
In this blog, we’ll explore what sets languages apart from dialects, how factors like mutual intelligibility and regional speech patterns affect localization, and why choosing expert Professional Translation Services is crucial to getting your message right in every market.
Language and Dialect: Breaking Down the Confusion
Many people often confuse languages and dialects because the distinctions can be blurred. Linguists describe this using the concept of a dialect continuum, where neighboring dialects are mutually understandable but gradually become unintelligible as they change across geographic regions.
For example, Serbian, Croatian, and Bosnian share a high degree of mutual intelligibility. However, political, cultural, and historical factors classify them as separate languages.
Similarly, language family classification adds another layer of complexity. Romance languages, such as Spanish, French, and Italian, share a common origin, whereas Germanic languages, like English, Dutch, and German, form another group. Even though languages in the same family share historical roots, their dialects can vary significantly.
Arabic serves as another clear example. Although it is labeled as a single language, its regional spoken forms differ considerably. Brands often need region-specific content. Working with professional Arabic Translation Services helps your message resonate in Modern Standard Arabic and the dialects people speak.
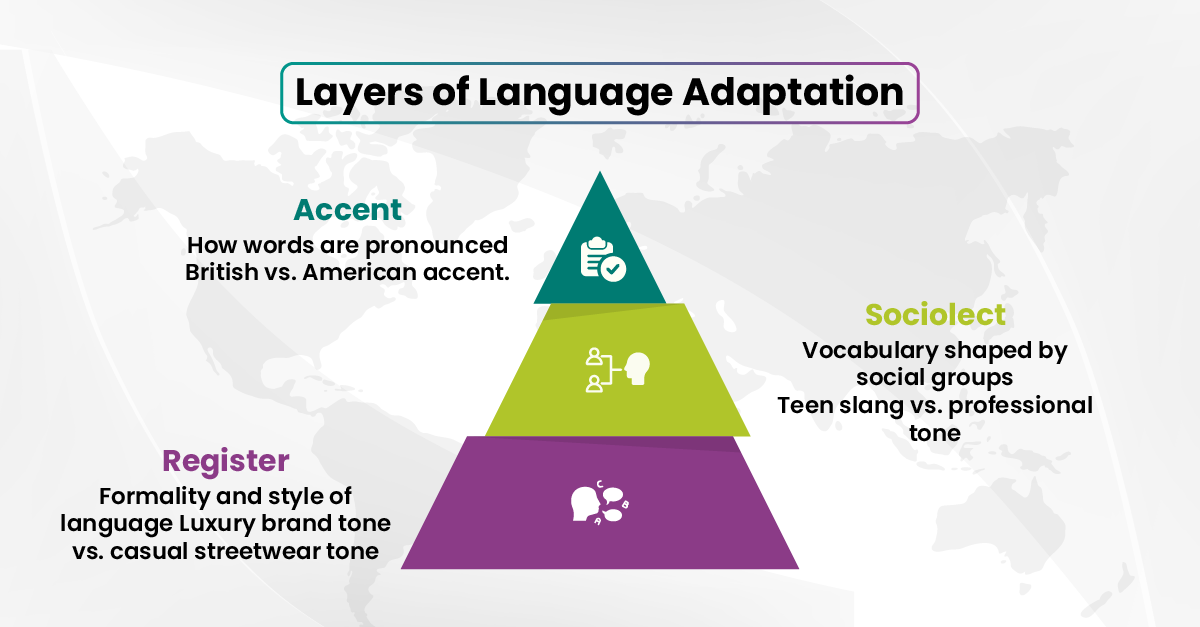
The Role of Accent, Sociolect, and Register in Localization
Localization involves adapting all aspects of content, such as accent variation, sociolect differentiation, and register variation, to align with a specific audience.
- Accent variation: Audiences react differently to accents, particularly in voice-over or audio-based training. For example, a British English accent in an American ad can feel foreign, while a heavy regional accent in Spanish may limit audience connection.
- Sociolect differentiation: Different social groups use distinct vocabulary and expressions. A marketing campaign targeting Mexican teenagers may include slang and informal phrases, whereas a bank’s message sounds formal and authoritative.
- Register variation: Luxury brands employ refined, aspirational language, whereas streetwear brands rely on casual, relatable tones. Recognizing these nuances helps maintain alignment between translated content and brand identity, appealing to the target audience’s expectations.
Global Classification Systems and Why They Matter in Translation
Localization experts rely on global classification systems to keep translations consistent and accurate. They give translators and localization experts standardized rules and references to prevent mistakes and confusion across languages.
- ISO 639 codes assign standardized abbreviations to languages, making them essential in translation software that handles content properly.
- The Glottolog database catalogs thousands of languages and dialects, helping linguists pinpoint the exact variant needed.
- Orthographic standardization impacts how you spell words in non-Latin scripts, like Arabic or Chinese.
- Romanization systems convert script into the Latin alphabet, improving readability and SEO in multilingual contexts.
The High Cost of Getting Dialects Wrong in Global Markets
Brands that overlook dialect differences often pay the price. Regional word variations may offend or even confuse the target audience.
Consider code switching, where people naturally switch back and forth between two languages or dialects in many online and digital communications. If a localized website does not accommodate this practice, it may feel unnatural, negatively affecting the user experience and conversion rates.
Some brands rely solely on Modern Standard Arabic for their ads. However, in countries like Egypt and Morocco, people often connect more with their local dialects. Overly formal wording can make campaigns less engaging, which is why global marketers increasingly rely on language translation services with expertise in vernacular speech and regional nuance.
The Race to Save Dialects: Why Language Revitalization Should Matter to Brands
Around 40% of the world’s languages face the risk of extinction, many of which are dialects spoken by small communities. Brands supporting language revitalization efforts demonstrate cultural respect and social responsibility. This not only builds goodwill but can also open access to niche markets.
Global companies investing in documentation linguistics projects, like creating educational materials or digital tools in endangered languages, position themselves as allies to these communities. In return, they gain trust, brand loyalty, and long-term cultural relevance.
From Pidgin to Creole: Localization Challenges in Hybrid Languages
Hybrid languages, such as pidgin and creole, present unique localization challenges. For example, Nigerian Pidgin and Haitian Creole blend elements from multiple languages, often without strict grammar or standardized writing systems.
To localize for these communities, brands must work with native linguists who understand local expressions and cultural context. This expertise is especially crucial in subtitling, voiceovers, and marketing campaigns where tone and phrasing significantly influence audience response.
Making the Right Linguistic Choices for Global Growth
Understanding languages and dialects is a foundation for successful international marketing and communication. Every detail, from how dialects change across regions to sociolect differentiation, standardized language codes, and even language revitalization, can shape how well your message connects with audiences worldwide.
TransPalm helps global brands navigate this complexity with accuracy, providing expert guidance to avoid costly misunderstandings, build genuine connections, and stand out in competitive markets.
Explore our Professional Translation Services and speak with a localization expert to convey your brand message across languages and dialects.





