Businesses are crossing borders faster than ever. Success in international markets depends on meaningful connections. And nothing builds that affinity like language.
Translation strategies deliver messages with clarity, emotion, and cultural relevance. Done well, they make audiences feel understood; neglected, they lead to confusion, cultural missteps, and lost opportunities.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore key types of translation strategies, their real-world applications, the tools and techniques that drive success, and how professional services can help your business thrive globally.
Why Effective Translation Matters in Global Business
Launching in new markets brings some challenges, especially if your message doesn’t translate well. A tagline that resonates locally might offend or confuse your target audience. It happens more often than you think.
That’s because translation isn’t just linguistic; cultural sensitivity in translation is critical to preserving your brand voice, avoiding costly mistakes, and building trust across markets.
With smart translation strategies, you can:
- Avoid loss of meaning in translation by capturing nuance.
- Adapt content for cultural relevance while keeping fidelity to your original message.
- Ensure consistency in translation across documents, platforms, and campaigns.
By applying proven strategies, you translate experiences.
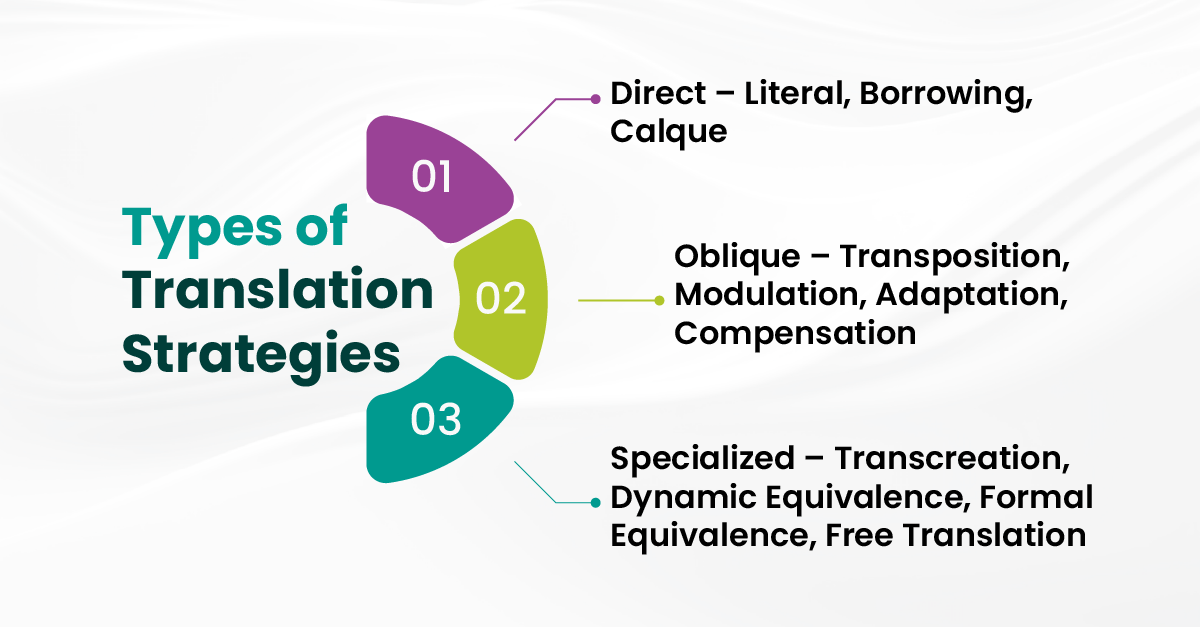
Types of Translation Strategies
Direct Translation Strategies
These are literal approaches to translation. They aim to maintain the original structure and meaning as closely as possible, which works well for highly technical or universal content.
- Literal Translation: Word-for-word communication from the source language to the target language (e.g., technical manuals and legal texts).
- Borrowing: Using foreign words from the source language directly in the target language without translation (e.g., “karaoke” in English).
- Calque: Translating idioms, technical terms, compound words, or phrases by substituting each element with its equivalent in the target language (skyscraper from German Wolkenkratzer).
2. Oblique Translation Strategies
These methods allow translators to restructure or rephrase to preserve the message’s intent, style, and cultural relevance in the target language.
- Transposition: Switching grammatical structures (e.g., noun → verb).
- Modulation: Changing the viewpoint or perspective (it’s not cheap → it’s expensive).
- Adaptation: Substituting cultural references with ones familiar to the target audience (Thanksgiving → local harvest festival).
- Compensation: Adding meaning elsewhere to maintain intent.
3. Specialized Strategies
These are used when content needs creativity, emotional, cultural, or stylistic weight.
- Transcreation: Rewriting the text to evoke the same emotional response as the original (e.g., ads, poetry, brand taglines, and slogans).
- Dynamic Equivalence: Focus on meaning rather than word-for-word translation (e.g., conversation and stories).
- Formal Equivalence: Staying close to the source text in words and structure (e.g., legal documents, academic works, and religious texts).
- Free Translation: Prioritize the main ideas over the exact words or structure, like explaining concepts.
Effective Translation Strategies for Different Content Types
Literary Translation
It’s about capturing the artistic intent, tone, and style of the original text. Two main strategies:
- Domestication → Make the text feel natural for local readers.
- Foreignization → Keep the cultural reference and style to experience the original culture.
Technical Translation
Technical content requires effective terminology management and translators who are familiar with the correct technical terms in both languages to maintain contextual relevance and avoid confusion or errors.
Legal Translation
Legal content demands absolute accuracy because mistakes can have serious consequences. Translators use formal equivalence, staying as close as possible to the original text, and must understand the legal systems and terminology in both countries to avoid risks.
Marketing Translation
Ads, websites, social media posts, and brand slogans need to resonate with the target audience’s culture and values.
This often requires creative rewriting, known as transcreation, rather than literal translation. For example, a slogan like “Finger Lickin’ Good” may need a completely new version in another language to trigger the same positive feeling.
Medical Translation
Medical translation involves life-critical content, like patient information, prescriptions, medical reports, and clinical trial documents.
Accuracy can save lives, while mistakes may put patients at risk. Combining AI-assisted translation with human expertise upholds patient safety, regulatory compliance, and clarity in multilingual healthcare settings.
Overcoming Common Translation Challenges
Untranslatable Words
Some words or expressions lack direct equivalents. Translators tackle this using:
- Borrowing → Keeping the original word in the target text.
- Paraphrasing → Explaining the concept of the word or expression.
- Cultural substitution → Replacing with a culturally relevant term or concept in the target language.
Idioms and Cultural References
Idioms often don’t survive literal translation. For example, “break the ice” may require a new expression in the target culture to preserve its meaning.
Tone and Style
Preserving the original tone is crucial, particularly in legal, medical, or marketing content. Here, proofreading strategies and editing strategies ensure fidelity and professionalism.
Ambiguity in Translation
Unclear context or multiple possible meanings can lead to errors. Translators address this by:
- Conducting contextual analysis
- Collaborating with subject matter experts to clarify technical or domain-specific terms
- Applying equivalence-based strategies to preserve the original meaning
Tools and Technologies Driving Modern Translation
Translation Memory (TM)
Reuses previously approved translations for consistency in translation and faster turnaround.
CAT Tools
Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) software offers terminology management, grammar adjustment, and built-in QA in translation for error-free results.
Machine Translation and Post-Editing
Neural machine translation (NMT) speeds up large-scale projects. Human post-editing ensures final content meets professional standards.
Discover how we combine these tools with human expertise in our Professional Translation Services.
Why Choose Our Professional Translation Services?
1. Expert Linguists
Native speakers with domain-specific expertise in legal, medical, and technical fields.
2. Customized Translation Strategies
Tailored solutions for translating for SEO, localizing software, e-learning localization, and more.
3. Rigorous Quality Assurance
Multi-step QA including semantic translation and communicative translation.
4. Advanced Technology
Use translation memory systems, translation management systems, and AI-assisted translation for speed and accuracy.
Unlock Global Markets with Proven Translation Strategies
Effective translation strategies are the backbone of successful global communication. They ensure your brand speaks not just in another language, but in a way that feels natural and relevant to your audience.
Ready to elevate your global communication? Contact us today for professional translation services designed to help your business thrive in any market.





